Emdadul Haq
Lecturer, Department of Textile Engineering, Primeasia University; Bangladesh
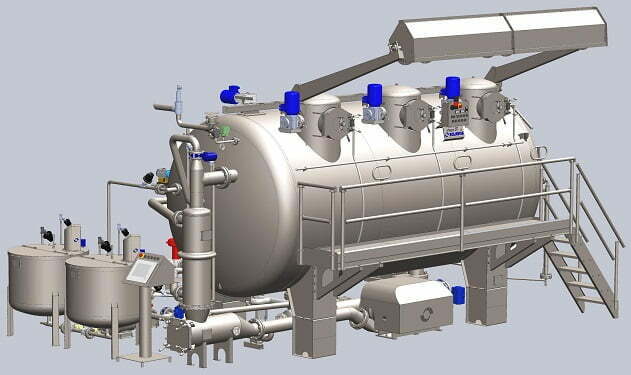
Effluent Treatment Plant or ETP is one type of waste water treatment method which is particularly designed to purify industrial waste water for its reuse and it’s aim is to release safe water to environment from the harmful effect caused by the effluent. Industrial effluents contain various materials, depending on the industry. Some effluents contain oils and grease, and some contain toxic materials (e.g., cyanide). Effluents from food and beverage factories contain degradable organic pollutants. Since industrial waste water contains a diversity of impurities and therefore specific treatment technology called ETP is required. The ETP Plant works at various levels and involves various physical, chemical, biological and membrane processes to treat waste water from different industrial sectors like chemicals, drugs, pharmaceutical, refineries, dairy, ready mix plants & textile etc.
Process Sequence of Effluent Treatment Plant:
Equalisation Tank
⇓
Storage & Homogeneous Tank
⇓
Neutralisation Tank: Sulphuric Acid Dosing Area
⇓
Distributor/ Biological Feeding Tank
⇓
Biological Oxidise Tank
⇓
Water Decolorant Dosing Tank
⇓
Sedimentation Tank
⇓
Excess Sludge Thickener Tank
⇓
Sludge Return Tank
⇓
Main Outlet Tank: Treated Water
⇓
Sludge De-watering
⇓
Polymer Mixing Tank
⇓
Dry Sludge Tank
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: