Garment Merchandiser | Tasks: Merchandising is any practice which contributes to the sale of products to a retail consumer. At a retail in-store level, merchandising refers to displaying products that are for sale in a creative way that entices customers to purchase more items or products.
A Garment merchandiser for clothing acts as a link between the industry and the consumer. He is responsible for managing every task, including purchasing the raw materials needed to complete the product, creating and finishing the garment, creating paperwork, and finally delivering. He is actually the principal person in charge of ensuring that the product is made on time.
A Garment merchandiser serves as a liaison between the buyer, numerous company departments, and affiliated businesses to facilitate the execution of the order. By “allied companies,” we mean “factories for stitching,” “fabric, accessory, and embroidery firms.” These can be outsourced and need not be actual homes. The Garment merchandiser must be aware of what is expected of him in order to contribute to the business and succeed on the market.
The garment merchandiser’s job is to manage the order from the moment the buyer places the purchase through shipping, determining account profitability, and receiving payment in the bank. In a nutshell, a Garment merchandiser evaluates, plans, acquires, handles, and supervises the complete order from beginning to end.
Types of Garment Merchandisers?
- Fashion Merchandiser: Fashion Merchandiser are who designs & develops process of Product.
- Production Merchandiser: Production merchandisers interact with customers, and their main responsibility is to fulfill tasks in accordance with their needs and promptly deliver finished goods to the customer’s location.
- Retailer Merchandiser: The retailer sells goods things in smaller amounts, acting as a middleman between the wholesalers and final customers. A merchandiser for retailers is both marketing and client manager. He establishes the location, timing, and amenities to move the products.
Roles of a Fashion Merchandiser?
- Create visually appealing displays that are appropriate for our target audience, our budget, and current fashions.
- Make a monthly plan and budget for visual merchandise at several places.
- Store layouts should be planned, sourced, and implemented with care.
- Get the clothing, accessories, and shoes you’ll need to finish your creations.
- Work together with distributors, suppliers, and fashion designers to finalize deadlines and negotiate contracts.
- Discuss the requirements for the campaigns for advertising in close collaboration with the marketing division.
- Attend trade events, seminars, and fashion shows on behalf of the company.
- To discuss sales reports and customer opinions, schedule a meeting with the sales manager.
- Make sure there are adequate resources and items in each store to finish the visual displays.
Roles & Responsibilities of a Fashion Merchandiser?
Roles of a Production Merchandiser?
- Proto Sample Order Query: First stage where the buyer will investigate about the order from the Merchandiser.
- Forwarding TechPack: After conducting the order inquiry, the buyer will provide the seller a “Tech Pack” or technical specification sheet. The tech pack contains all the information on a certain look and the goods.as follows:
- measurements;
- fabric;
- a style code;
- surface decoration details;
- product style
- design; etc.
- Product Development: It is one of the garment merchandiser’s key responsibilities. After receiving the “Tech Pack,” the merchandiser will set up the technology. He gives junior merchandisers advice regarding the buyer’s specifications and needs. By doing so, the junior merchandisers can help with the sample Department coordinator/manager. The sample was created in accordance with the customer. The efficient exchange of ideas among the many People’s levels are crucial for sample development.
- Approval of the Developed Sample: 2-3 Samples are sent to buyer to approve. The development sample’s primary goal is for the buyer to comprehend how the garment style looks in more depth and to gauge the manufacturer’s capability and ability to produce the sample for their line. The samples are created with in-stock fabric that closely follows the exact specification. The buyer will better comprehend the manufacturer’s capabilities thanks to this. Sometimes, in order to fulfill the order, the merchandiser merchandiser additionally creates a sample using unique cloth. Surface ornamentation and fit are kept to throughout sample development in accordance with the tech pack. If a correction needs to be made, the buyer must supply the necessary information, after which the samples are once more worked on/developed and sent to the buyer. This procedure will be carried out until the samples get approved.
- Costing: Once the sample gets approved, next job is to make costing. The costing includes Fabric Costing, Trims & Accessories Costing, CMT, Washing & Finishing Costing, Bank Charges and Miscellaneous cost.
- Order Placement: Once the negotiation is done, the order is placed by the buyer with the details of required order quantity & specification.
- Fabric & Trim Ordering: After that, the Garment merchandiser will place the necessary order materials such as cloth, trims, accessories, etc., according to the color, GSM, weave, quantity, quality, etc., that are necessary for the style.
- Lab Dip: After the order is accepted, the initial procedure is a lab dip where the seller will provide the buyer samples of colored fabric for analyzing colors. Numerous colors of the submitted fabric and lab samples are the garment’s requested color from the buyer. The crucial step is lab dip approval; this procedure will be kept going until the customer gives the shades their approval. This Fabric will be dyed in bulk using an approved shade for final clothing creation.
- Fit Sample: After the Lab dip, Fit Sample is produced, which is made of actual Fabric or actual fabric close to the buyer requirement. This sample is generally made with medium size.
- Pre-Production Sample: Once the fit sample is approved, PP (Pre-production) Sample is made which is also known as Red Sample. This sample is made of actual fabric from buyer’s requirement.
- Size Set Sample: Till the PP Sample, the sample may be developed in smaller scale , but most of the case, buyers want the Size set sample to be developed in actual production area. Size set samples are made for the purpose of checking the different sizes of the same style in terms of fit, measurements, styling, etc.
- Pre-Production Meeting (PPM): The garment merchandiser will schedule the pre-production meeting once all samples have been approved and all raw materials are available in the shop to begin the bulk production. All department heads and key company personnel will gather for a pre-production meeting to plan the production. Here, the merchants will talk with the production managers on how the production can be scheduled and completed within the necessary timeframe in order to avoid delays. Therefore, this conference is crucial and necessary.
- Forwarding of production file to production planning and control: Production file is a necessary document which includes: Measurement, Export Order Sheet, Packing type, Style Description, Marker Plan, TNA order sheet, 2D style diagram & trims etc.
- Checking the availability of fabric & trims: Once the file is received by the PPC, they will check and study each and every detail in the file and they will also check the availability status of the fabric and trims in the store. They will follow-up on the same if it’s not yet reached in the house.
- Checking the ornamentation of the particular fabric: Surface ornamentation may include embroidery, printing or applique and these are done as per the buyer’s requirement, so PPC will check the ornamentation details and plans according to that and in parallel arrange all the required things for the same.
- Checking the stitching material in house: Stitching materials are those which are used for sewing like threads and accessories which assist production so in parallel they will do the arrangement for the stitching materials in-house.
- Checking the pattern with master: Production file includes all the details about the patterns and merchants will forward the original patterns along with the production file to the PPC. Once they receive the patterns, they will forward the patterns to the pattern master and master will cross check the pattern with the actual and confirm.
- Grading & Final Cross Check: Once everything is checked and confirmed by the master then, the pattern is forwarded to the CAD (computer aid design) department for grading. Grading is a process of making different sizes from a basic size.
- Laying & Cutting: Production planning will provide instructions for this process depending on the order amount, the length of the lay, the number of lays, and the type of lay to be dispersed department. The created pattern lay-out obtained from the marker plan is used to cut the materials once the pattern has been laid.
- Wash: After cutting, the fabric is sent to washing department if it requires, the garment merchandiser need to check whether it is matching with buyer’s requirement.
- Bit Printing/ Applique/ Embroidery: Once the garment wash is finished, the fabric is sent to embroidery department if it demands.
- Loading in time: Once the surface ornamentation is over, the cut pieces are bundled & sent to the sewing department, A garment merchandiser needs to follow up the time schedule of this loading.
- Finishing: Once the whole garments are stitched, the stitched garments is forwarded to the finishing section. A garment merchandiser needs to follow up every line of finishing if buyer’s requirement is being met or nor, or to what extend deviation is happening.
- Dispatch: Dispatch is the end process in which the garments are packed in the cartons and shipped. It is garment merchandiser’s responsibility to check the availability of required documents for logistics and shipping process.
Roles of a Retail Merchandiser?
Another form of merchandising activity that takes place at the bottom of the hierarchy is retail merchandising. Here, the retail merchandiser acts as a middleman between wholesalers and final consumers by selling goods in smaller amounts. Marketers and customer service representatives are both store merchandisers. He arranges the venue, timing, and resources needed to conduct the sale. The following are the generalized duties of retail merchandisers:
- Planning product ranges in close collaboration with customers and other merchandisers
- Meeting with distributors, analysts, and suppliers
- Handling finances
- Estimating revenue and earnings
- Quantities and delivery schedules are negotiated
- Monitoring and educating subordinate employees
- Controlling stock distribution and levels
- Addressing supply and production issues as they occur
- Determining the proper stock promotions and price reductions
- Presenting financial data to senior managers
- Evaluating the sales performance of various ranges.
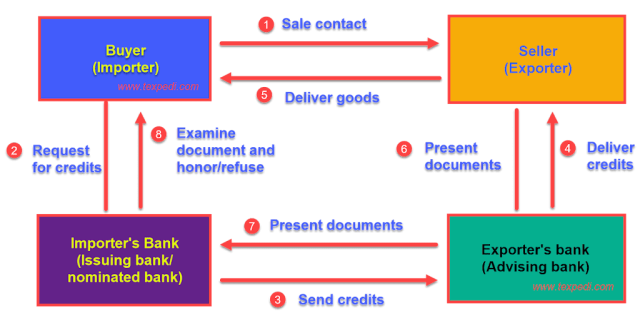
Flowchart of a Retail Merchandiser?
Conclusion
Check out these related articles: