Supply Chain
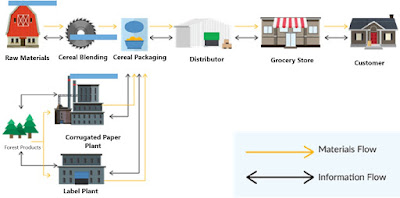
A supply chain is a network of individual functions within an organization that begins with the development of a strategic plan and ends with the delivery of a product or service. Those functions are listed below:
Warehousing Operations
Warehousing personnel perform the receipt, storage, retrieval, and distribution of procured goods and materials. Initially, goods and materials are received from suppliers into a warehouse by warehousing personnel who unload trucks, inspect items to ensure there is no product or shipping damage, and process the items (now formally part of inventory) to a storage location until they are needed. Once there is a demand for the stored inventory, warehousing personnel retrieve or pick the inventory and deliver it to the intended destination, such as manufacturing for assembly.
As manufacturing personnel complete their assembly operations, they process raw materials and semi-finished goods, sending finished products back to the warehouse. At this point, products could be stored for further assembly operations or might be packaged and prepared for immediate delivery to a customer.
Warehouses are not always standalone facilities. In some cases, the storage of raw materials, work in process, and finished goods use dedicated portions of the manufacturing facility to expedite the movement of inventory through the various manufacturing processes. In other cases, warehouses and distribution centres may have roles that are entirely distinct from manufacturing operations and focus on storage and order fulfilment.
Warehousing operations can be simple floor storage or can include various types of racking for high storage. Many facilities feature sophisticated, automated material handling systems to increase speed and accuracy while reducing costs. Functions performed within warehouses or distribution centres have increased significantly, so this function now plays a greater role in the overall supply chain. From picking items to repacking them into multipacks and shipping individual orders or full truckloads, the complexity of warehousing has resulted in a greater focus on the efficiency of these operations and how they impact the deliveries of customer orders.
Warehouses designed to function as distribution centres can provide additional (value-added) services for customers. These could include services like cross-docking and kit assembly. Cross-docking generally moves incoming products directly to outgoing trucks, thus eliminating the need for storage entirely. Kit assembly is performed to pick multiple items and place them into one kit or container for processing to be sent to manufacturing; this enables the manufacturing assembly operation to assemble the final product easily.
Warehousing is supported by a warehouse management system (WMS) that is linked to a company’s ERP system. The WMS is integrated with the material handling systems, which includes equipment to move, stock, pick, and route goods in and out of warehouses and distribution centres. These material handling systems feature specialized software that enhances the flow of information and communication to optimize the efficiency of warehouse processes.
Reference: Warehousing Operations Certification Track. LINCS in Supply Chain Management Consortium. May 2016. Version: v2.22. www.LINCSeducation.org.
Reference: Warehousing Operations Certification Track. LINCS in Supply Chain Management Consortium. May 2016. Version: v2.22. www.LINCSeducation.org.
Fahad Mahmud
Lecturer (Technical), Department of textiles at SKTEC
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: