E-textiles are mostly known as the electronic textile or smart textiles, is a kind of fabric that has the ability to conduct electricity. The majority of the time, conductive elements are included in the fabric to form an e-textile. There are several industries and uses for e-textile that are beneficial to both humans and all other living organisms on the planet. We’ll talk about the electronic textile in detail here, which is a notable advancement in the smart textiles’ application area.
 |
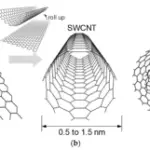
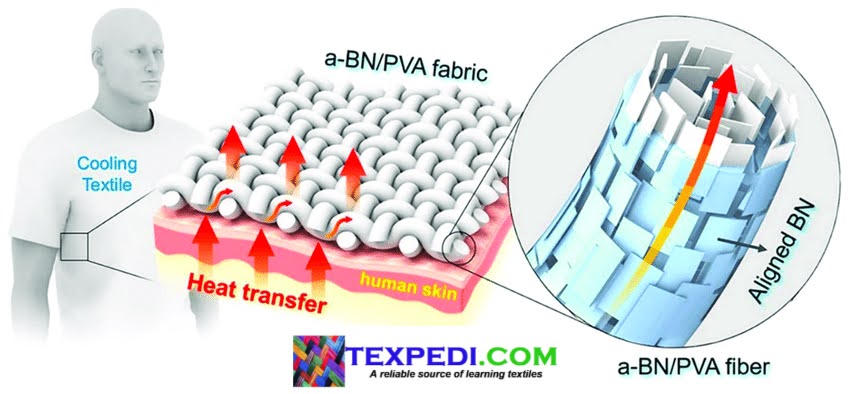
| Figure 1. E-textiles | Electronic textiles | smart textiles |
What is E-Textile or Electronic Textile?
E-Textile is a kind of fabric that incorporates electrical components to allow for conductivity and the usage of a variety of technologies. Electronics and connectivity are woven into these textiles, allowing them to be physically flexible and small. With electrical components, it may react to changes in its surroundings by emitting light, sound, and even radio waves.
E-textiles are possible to be worn in daily scenarios where present wearable computers would be inconvenient for the user. When it comes to power conservation and context awareness, E-textiles have a significant advantage over traditional textiles because of their ability to quickly adapt to the changes in the computing and sensing needs of an application.
How is E-textile made?
Electronic textiles may either be embedded or laminated, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. E-textiles that incorporate circuitry into the fabric are known as “embedded e-textiles.” Additionally, conductive textiles may be created by simply printing on a conductive route. Textiles have a greater influence on this industry than electronics.
In the case of laminated electronic textiles, circuitry is printed or manufactured on even a non-textile foundation and then sewn or bonded to the fabric. For the most part, this industry is a by-product of electronics rather than textiles.
Types of E-textiles
In terms of electronic textiles, there are two primary categories:
- Inside textiles are traditional electrical components, including wire, integrated circuits, light-emitting diode (LED), and conventional batteries.
- Incorporating electronics into the method involves electronic textiles. Active constituents like transistors, semiconductors, and solar cells may also be included in this category of components.
Advantages of E-textiles
- Sensors and computers become more flexible, light, and comfortable to wear as a result of the use of electronic textiles.
- The circuitry may be almost undetectable, allowing the user to maintain a feeling of secrecy.
- Since the majority of circuits implanted in fabrics are roughly the diameter of a single sheet of paper, there is no need for the user to bother about handling cables or wires.
- Fabrics have a high resistance to compression and impact damage, which allows their integrated circuitry to operate with more flexibility and longevity.
- E-textiles include intelligence characteristics, or they may “borrow” computational power from a smartphone via connectivity with the device.
Demand of E-Textiles
According to market analysis, the textiles industry for e-textiles is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 30.4 percent from 2017 to 2025. During the years 2011-2015 to 2015-2020, consumption of Passive, Active, and also very smart e-textiles surged dramatically and is predicted to continue to climb through 2020-2025. Naturally sourced textile materials don’t transmit electricity, and as a consequence, the manufacturing costs of these materials are much higher.
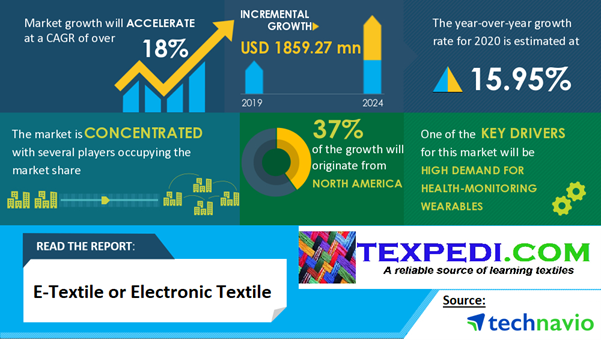 |
| Figure 2. Market demand for electronic textiles. |
As a consequence, regular metal, as well as alloys, deliver significantly superior conductivity at a lower cost than any textile-integrated material, which is a drawback. Carbon fibres have been more important in recent years, and they might be quite valuable in the future. An integrated textile temperature sensor might be a lifesaver in the present pandemic crisis when thermal monitoring is a vital consideration.
Application of E-Textiles
The usage of e-textiles will very certainly become commonplace in the near future. Moreover, at present, it is being used to create various applications in different textile sectors. As an example of e-textile as clothing, consider a shirt that measures the user’s heart rate on a routine basis while they’re exercising or workout and connects to a mobile application.
E-Textiles are also widely used in the medical sector to make several applications. Compact, light, and fashionable wearable medical gadgets that monitor oxygen saturation or other tough health parameters as well as automatically convey alarms to a medical team. With e-textiles, manufacturers may design new product categories that can collect data, send it, and connect with the customer, wearer, or third party.
Final Thought
E-Textile or electronic textile is a kind of smart textile that is a kind of fabric. In the context of electronic textiles, a textile substrate with built-in sensing capabilities is referred to as electronic textiles. Digital components such as miniature computers and electrical devices may be included in this textile. Recently, electronic textiles are using in different textile sectors. In future we will detailly talk about the smart textile and its application as well.
Author courtesy:
Md Mahedi Hasan
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering (Apparel Engineering)
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali, Bangladesh
B.Sc. in Textile Engineering (Apparel Engineering)
Textile Engineering College, Noakhali, Bangladesh
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: