Technical textiles, designed for specific purposes other than clothing or home furnishing, serve various sectors. Examples include automotive, medical, geotextiles, and protective clothing. These textiles boast unique properties and characteristics. They are manufactured using advanced techniques and innovative materials, offering features like high strength, UV protection, and water repellency.
Consequently, they play essential roles in healthcare, construction, transportation, and aerospace. Technical textiles continuously evolve through research and development. They drive innovation and progress, enhancing safety, efficiency, and performance across industries.
Types of Technical Textiles
There are several types of technical textiles. Geotextiles, protective textiles, medical textiles, automotive textiles, sports textiles are special types of it.
a) Geotextiles
Geotextiles, accordingly, are permeable fabrics used in geotechnical applications. They serve multiple functions, including filtration, drainage, reinforcement, separation, and stabilization. These textiles consist of synthetic materials like polyester or polypropylene and come in various weights and textures for specific needs. Moreover, engineers use them to enhance various geotechnical structures effectively and affordably. Furthermore, these fabrics play a crucial role in creating secure and sustainable infrastructure. Not only do they filter water to prevent soil migration in road embankments, but they also drain water from landfills, reinforce slopes, separate soil types in construction, and stabilize areas prone to landslides or earthquakes. All in all, geotextiles offer a versatile and economical solution for optimizing geotechnical projects. Therefore, they empower engineers and designers to construct enduring and reliable structures.

b) Protective and Functional Textiles
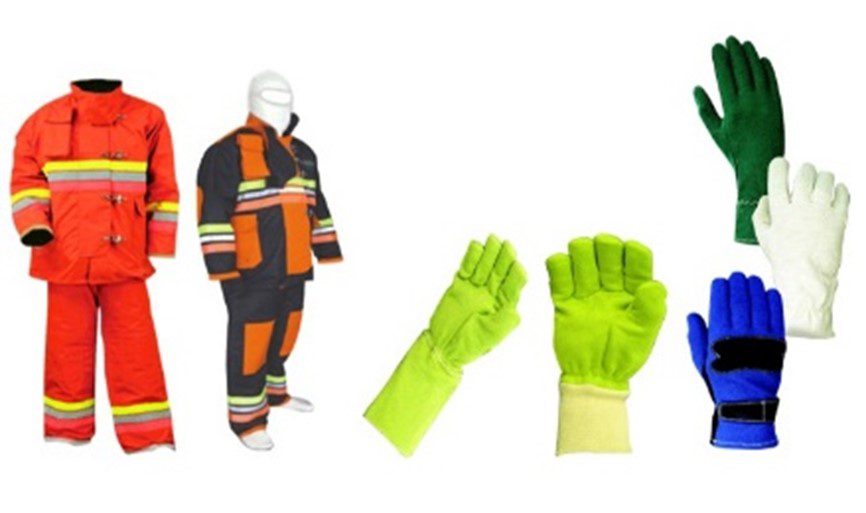
Protective textiles are crucial for safety. Additionally, they offer defense against various hazards, including fire, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. They find applications in firefighting, the military, and industrial workplaces. Examples include bulletproof vests, flame-resistant clothing, and chemical-resistant suits.
These textiles are constructed from robust, durable materials, allowing them to endure harsh conditions. Moreover, functional textiles go beyond their basic properties. They possess specific functionalities like moisture-wicking, antibacterial capabilities, UV protection, and conductivity. They are used in diverse sectors, including healthcare, sports and fitness, and electronics, where technology integration is vital.

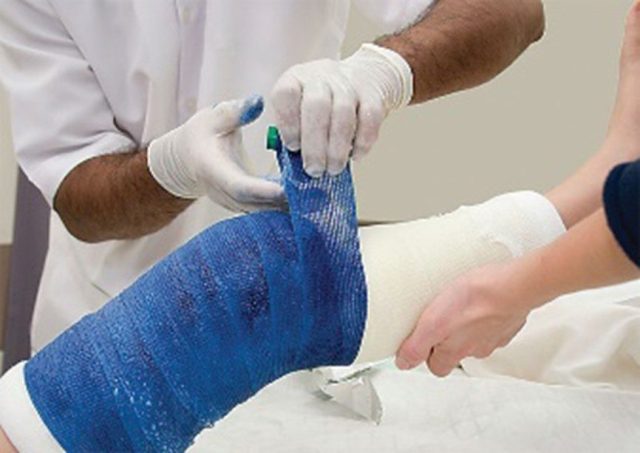
c) Medical Textiles
Medical textiles, whether in the form of fabrics or textile products, find use in healthcare and medical applications. These textiles must meet specific requirements, including biocompatibility, sterility, and barrier properties. Moreover, medical textiles are employed in various applications, including surgical gowns, wound dressings, implants, bandages, and hygiene products such as diapers and sanitary napkins. Researchers are particularly interested in healthcare monitoring for patients and the elderly, who require ongoing medical support. Not only are wearable monitoring systems of interest, but also the advancement of these systems to track vital signs and other essential physiological indicators is a significant focus. Numerous research projects in Europe have been dedicated to the development of wearable biomedical garments with various sensor technologies, aiming to enhance the mobility and care options for these individuals.
Automotive textiles serve a dual role in vehicles, both in their interiors and exteriors. They enhance comfort, safety, and aesthetics. Moreover, these textiles are meticulously crafted to adhere to the stringent requirements of the automotive industry, including durability, UV resistance, flame retardancy, and sound insulation.
Examples of automotive textiles encompass seat upholstery, carpets, airbags, and headliners. Notably, seat upholstery stands out as a primary application, selected for its comfort, durability, and resistance to wear and tear. These textiles are meticulously engineered to endure frequent use, ensure proper ventilation, and provide a luxurious feel. Furthermore, they undergo rigorous testing to meet safety standards and comply with flame retardancy regulations.
d) Sports Textiles
Sports textiles, above all, aim to boost athletes’ performance, comfort, and protection. Additionally, they incorporate features such as moisture management, breathability, and flexibility. All in all, sports textiles find applications in sports equipment, athletic apparel, footwear, and accessories.

Sports textiles are uses in sports, the sportswear items.
These types of technical textiles serve specific functions. Additionally, they are tailored to meet industry demands. Moreover, continuous development and innovation in materials and manufacturing techniques contribute to the evolution of technical textiles. This evolution enables their wide-ranging applications in numerous sectors, all in all.
Summary of Application of different Types of Technical Textiles
| Technical Textiles | Applications |
| Geotextiles | Soil stabilization, drainage |
| Protective and Functional textiles | Firefighters’ gear, bulletproof vests |
| Medical textiles | Wound dressings, surgical gowns |
| Automotive textiles | Car seat upholstery, airbags |
| Sports textiles | Athletic apparel, sports equipment |
Properties of different Technical Textiles
Technical textiles possess a wide range of properties that make them highly versatile and suitable for various applications. The properties of different types of textile are get materials special characteristics.
| Property | Description |
| Tensile strength | Ability to withstand pulling forces |
| Permeability | Allows the passage of liquids and gases |
| UV resistance | Ability to resist degradation from sunlight |
| Tear resistance | Resistance to tearing and puncture |
| Soil retention | Ability to hold soil particles in place |
| Property | Description |
| Flame resistance | Ability to withstand and not contribute to fire |
| Abrasion resistance | Resistance to wear and tear |
| Ballistic protection | Ability to stop bullets and projectiles |
| Property | Description |
| Biocompatibility | Compatibility with living tissues |
| Sterilizability | Ability to be sterilized without damage |
| Moisture management | Regulation of moisture levels |
| Barrier properties | Resistance to penetration of bacteria and fluids |
| Skin-friendliness | Non-irritating and comfortable for the skin |
| Property | Description |
| Durability | Resistance to wear and fading |
| Colorfastness | Ability to retain color despite exposure to light |
| Flame retardancy | Ability to resist combustion |
| Water resistance | Repels water and prevents absorption |
| Sound insulation | Reduces noise levels inside the vehicle |
Others Applications
a) Agrotech offers product designed that agricultural, horticultural, gardening purposes.
b) Buildtech, the ingenious architect of innovation, crafts a kaleidoscope of bespoke marvels catered to the grand tapestry of membrane structures, lightweight masterpieces, terraforming triumphs, fluidic engineering wonders, and the very veins of modern civilization, the arteries of road construction. Clothtech focuses on introducing innovative techniques and advancements in the manufacturing of shoes and clothing.
c) Geotech weaves the threads of innovation and durability to pave the way for road construction, civil engineering, and the fortification of dam and waste site projects with their cutting-edge textile products. Hometech brings forth innovations in the manufacturing of furniture, upholstery, floor coverings, and carpets.
d) Indutech offers a range of products suitable for mechanical engineering, as well as the chemical and electrical industries.
e) Sportech revolutionizes the sports and leisure industry with bespoke innovations meticulously crafted to enhance every athlete’s performance, redefine spectator experiences, and elevate the boundaries of leisure activities.
Technical textiles play a crucial role in various industries, providing advanced functionalities and performance characteristics that conventional textiles cannot offer. The tables presented in this assignment highlight the different types of technical textiles and their key properties, showcasing their diverse applications. The continuous advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques hold promising potential for further innovation in the field of technical textiles. The ability to tailor these materials to meet specific requirements opens up opportunities for enhanced performance, sustainability, and improved user experiences in various sectors. Approximately 65% of fibers utilized in textile applications consist of synthetic fibers, highlighting their significant presence in the industry. Within this sector, technical fibers have emerged as a crucial and highly relevant field.
Mahbub Alam Riaz
An undergrad student at BUTEX. He has a penchant for contributing to national dailies and currently holds the position of University Correspondent at the Daily Kalbela newspaper. You can reach out him at [email protected].
Check out these related articles: