Emdadul Haq
Lecturer
Department of Textile Engineering, Primeasia University; Bangladesh
Features of Plain or Single Jersey Knitting ( machine, process and structure):
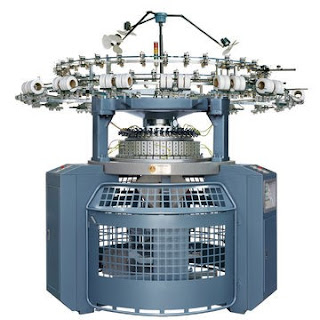
1. The machine has only one bed which may be flat or circular.
2. There is only one set of needles and one cam system in the machine.
3. Minimum one yarn is needed to produce a fabric.
4. Single faced structure, i.e. only one type of loops- face or back are visible on the surface.
5. Loops are V-shaped on the technical face and semi-circular on technical back of the fabric.
6. Because of side limbs of the loops on the face side, it feels smoother on the face side than the backside.
 |
| Single Jersey Circular Knitting Machine |
7. Knitted loops tend to distort easily under tension which helps to five form-fitting and comfortable.
8. Fabric shortens in width if the same is extended in length by tension and vice-versa.
9. The fabric has good extensibility in both length and width direction but width-wise extensibility is generally much higher than lengthwise extensibility.
10. Yarn/course can be unroved from starting and ending end of knitting
11. Fabric curls at the free edges on flat surface-toward the front at the upper and lower edges and toward the back at left and right edges. This curling is mainly due to the unbalanced yarn bending moment existing in the three-dimensional nature of the structure. Yarn bending rigidity property is responsible for curling.
 |
| Single Jersey Structure |
12. Because of stitch simplicity, the production rate is high and the machine is simple and cheap.
13. Stitch length can be varied with stitch cam setting.
14. Fabric shrinks in width/circumference and the extend of shrinkage is about in the range of 25-40%.
15. Course per inch and wales per inch in the fabric inversely varies with loop length.
16. Properties like rigidity, air permeability, bursting strength etc and GSM of the fabric change with change in loop length.
 |
| Laddering Effect |
17. Laddering takes place; laddering means disintegration of loops due to breakage of yarn as the intermeshed loops are held by each other at the cross-over points. The needle loops preferably unmesh down the wale.
18. Fabric thickness is approximately two times the diameter of the yarn used.
19. Sinker top machine is very common.
20. Common gauge is 16-28 for circular machines and 5-12 for flat machines.
Reference Book
- Fundamentals and Advances in Knitting Technology
- Sadhan Chandra Ray
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: