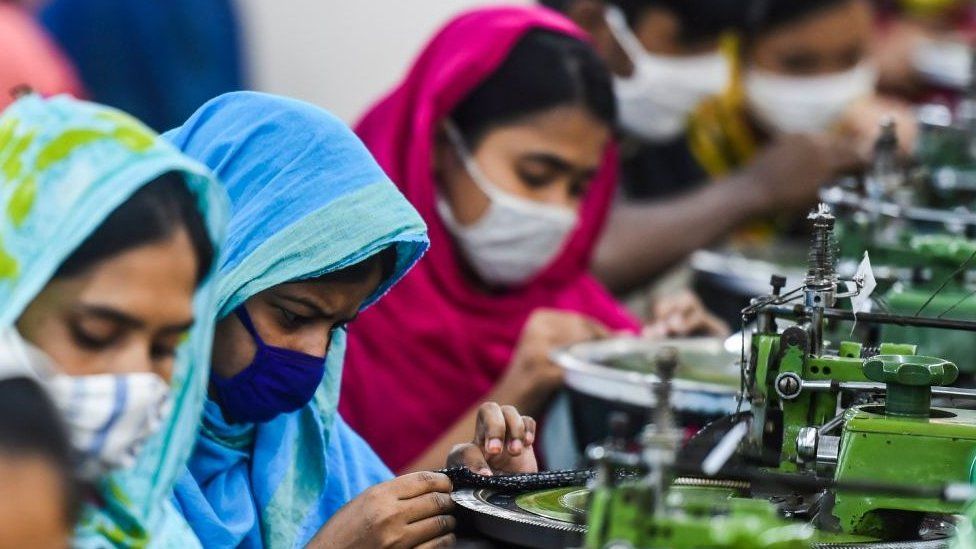
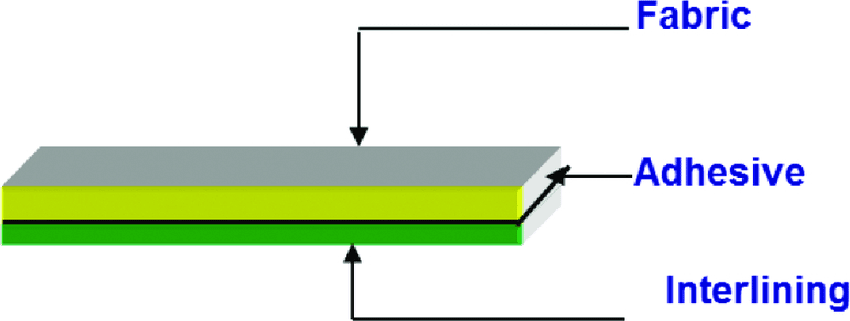
Fusing?
Fusing is a process of introducing interlining materials/sheet in-between the parts of the garment. Fusible Interlining sheet is coated with thermoplastic polymer resin and it is used to ensure a fixed shape, good strength and stability of a garment.
What are the controlling factors of fusing?
1. Temperature: There is a certain range of temperatures that are suitable for each type of resin. Too high a temperature causes the resin to become too viscous, which could result in the resin being forced through to the right side of the cloth. On the other hand, if the temperature is below a certain limit, the resin cannot be transferred into the garment parts fabric due to insufficient resin viscosity. The average range of applicable temperature for resin melt is 130-160℃.
2. Time: Time is another important controlling factor while fusing the interlining and the fusing duration depends on:
- Whether the interlining has a high –or low melt resin.
- The nature of the top cloth being used: thick or thin, dense or open?
3. Pressure: Most fusing machines use two steel rollers or pressure plates to create pressure. But recently, a flexible pressure system has been developed that adapts itself automatically to the changes in the thickness of fabric-interlining assembly and maintain even pressure on the entire assembly. When the resin is viscous, the pressure is applied to the top cloth-interlining assembly to ensure that:
- Full contact is made between the top cloths and interlining.
- Heat transfer is at the optimum level.
- There is an even penetration of the viscous resin into the fibres of the top cloth.
4. Cooling: Enforced cooling is used so that the fused assemblies (fabric + interlining) can be handled immediately after fusing. Cooling can be induced by various systems. For example, water-cooled plates, compressed air circulation, and exposure to a vacuum environment.
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: