Siro Yarn is manufactured by a method called Siro Spinning or Eli twist spinning. In this, the yarn is made into 2 plies on the ring spinning machine. Siro spun can be seen as a pseudo-two-fold yarn in which the two components are untwisted strands rather than twisted singles yarns. The CSIRO (Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization) in Australia came up with SIRO yarn, therefore it is called “Siro” spinning.
Siro Spinning System
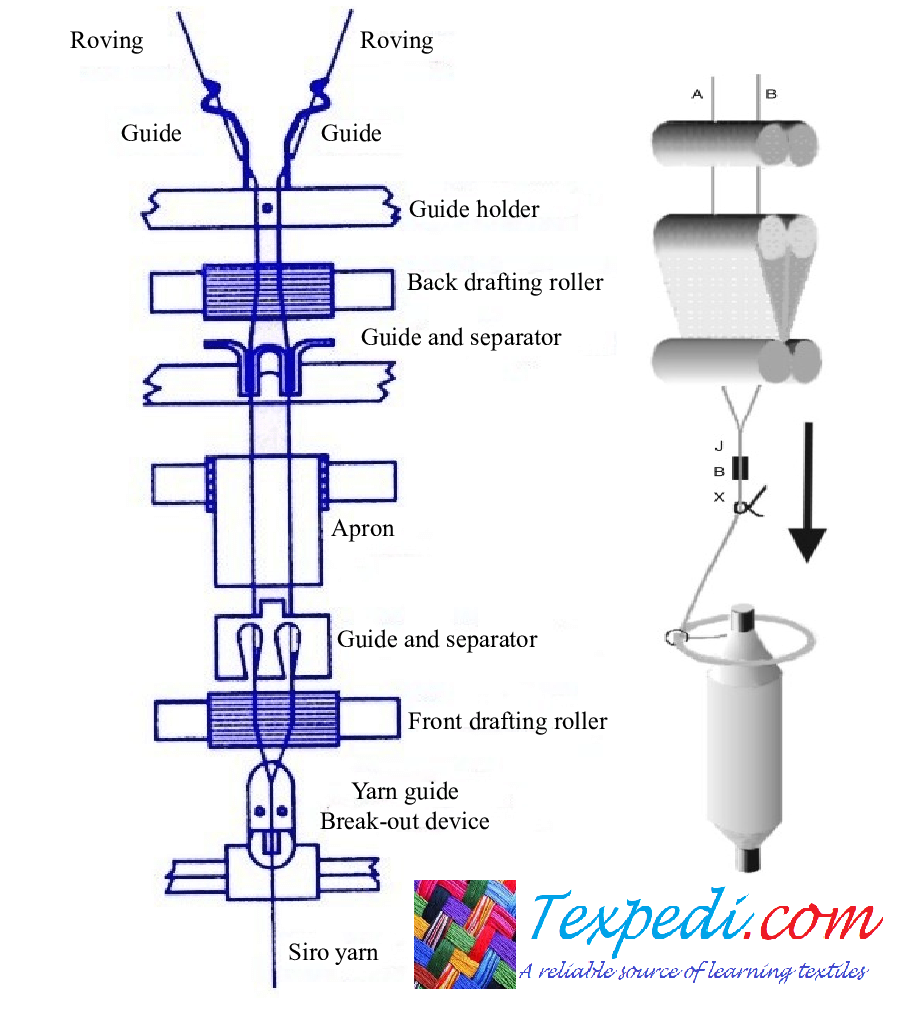
The Siro yarn technique applied a number of CSIRO’s self-twist findings to the conventional ring spinning technology of the worsted system. The SIRO spinning system incorporated spinning and doubling into a single operation. In this method, two roving are led concurrently through the drafting machine, separated by two specially designed condensers, and drawn independently (as shown in Figure 1).
Also, using a ring and traveler, the twist is introduced as with a typical single yarn. The drafted roving strands at the exit of the drafting mechanism, with some twist formed in the individual strands up to the nip point, are united to create a twofold-like yarn (shown in Figure 2). Numerous experts have found that the hairiness of Siro yarn fabrics has been drastically decreased.
 |
| Figure 2. SIRO Yarn |
The technological process of Siro spinning
Figure. 3 depicts the technical process and yarn path diagram of Siro spinning. The roving is fed into a ring frame with separators to ensure that each roving is drafted separately (or individually). The two strands that come out of the drafting mechanism twist together to form a single yarn that is called the Siro yarn. The following are the features of the Siro spinning technique: The ring spinning frame is readily adjustable; the structure of Siro yarn is comparable to that of plied yarn; and the yarn has greater abrasion resistance and is less hairy.
 |
| Figure 3. The technological process of Siro spinning |
The principle of Siro spinning
A regular ring spinning machine may be converted into a Siro spinning machine with little effort. The principal modifications are as follows:
- The creel is modified to accommodate an additional roving. Depending on the kind of spinning machine, the spindle space and roving building will vary. On the same bobbin, the two twist-less roving must be fed at distinct phase locations.
- Single-grooved yarn guides are replaced by double-grooved yarn guides with reasonable groove spacing.
- On wool spinning machines with a slip draft, the groove width of the middle leather roller rises from 18 mm to 24 mm.
- A break-out device, sometimes known as a BOD, is put in the space between the front roller and the yarn guide. The break-out mechanism may mechanically break another strand if one of the strands in the yarn is broken, preventing the manufacture of a single yarn. The equipment used to break out should have a high level of sensitivity and outstanding stability.
 |
| Figure 4. The principle of SIRO spinning |
Properties of SIRO Yarn
The SIRO yarns have more tenacity and elongation, as well as less hairiness, but they also have somewhat lower evenness and fault count ratings. However, the properties of SIRO yarns have been provided as below:
- Breaking Elongation: Higher elongation-at-break values.
- Evenness: U% and other imperfections like thick-thin places and neps are low.
- Lea strength: Extremely high CSP.
- Single yarn strength: Siro yarn has better single yarn strength.
- Voluminosity: Has greater diameter than conventional two-fold yarn.
- Twist: Low level of twist in siro yarn than conventional two-fold yarn.
- Abrasion: Slightly less abrasion resistant.
- Knot strength: Lower knot strength.
- Strip strength: Higher strip strength.
- Tearing strength: Higher tearing strength.
- Flexural rigidity: Less flexural rigidity.
- Crease recovery: Higher crease recovery angle.
- Breakage rate: SIRO yarn shows higher breakage rate as compared to the conventional two-fold yarns.
Limitations of Siro yarn
Excellent spinning performance does not ensure good weaving performance, which is the fundamental downside of Siro spinning. In SIRO yarn manufacturing, it cannot be said that if the spinning performance of the single yarn is excellent, the weaving performance of the two-folded yarn will also be satisfactory. In addition, it does not permit the use of a less expensive raw material, such as a coarser fiber. Some factories have made the Siro yarns with just 60 fibers in the cross section by using a longer, coarser fibre. The performance in spinning was satisfactory, however the performance in weaving was not acceptable.
When making Siro yarn, if front zone condensers aren’t employed, significant fiber loss (up to 5 percent) might occur. Using front zone condensers, this can be brought down to half a percent (0.5%). Siro yarns exhibit more thin places on the Uster evenness testing, which is likely due to the occasional loss of fiber.
Applications of SIRO Yarn
SIRO Yarn is particularly well-suited for the creation of lightweight trans-seasonal textiles; as a result, a sizeable amount of the world’s worsted spinning installations has been converted to this new and cost-saving CSIRO technology. The key applications of the SIRO yarns are as follows:
- Used almost exclusively in the production of weaving yarns.
- Fabrics woven from Siro yarns have consistently outperformed, or at least equalled, the conventional fabrics in terms of measured stiffness and assessed handle.
References:
- Handbook of Yarn Production, 2003 by Peter R.
Lord - Advances in Yarn Spinning Technology, 2010 by C.A. Lawrence
- Specialist Yarn and Fabric Structures, 2011 by R. H. Gong
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: