Shah Md. Maruf Hasan
Lecturer, Department of Apparel Engineering, BUTEX
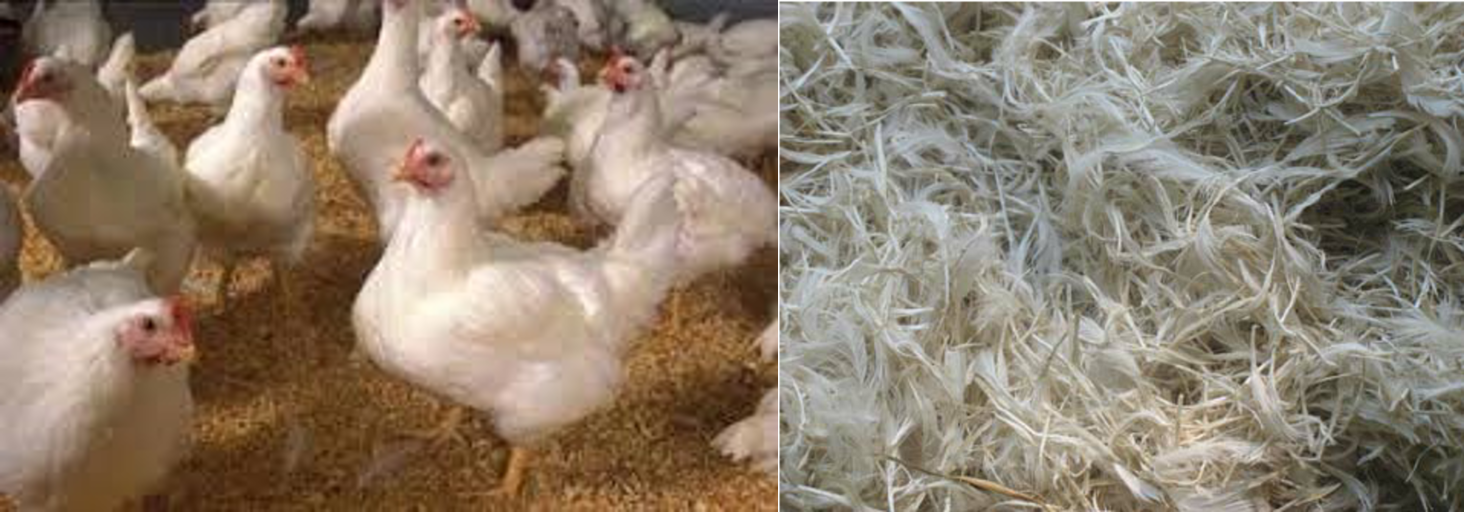
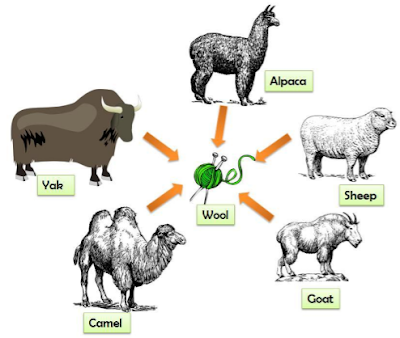
Wool is the natural protein fibre produced from the animal hairs. Animal hair consists of complex proteins. The hair of sheep and goats is particularly important for textile. Wool is the animal fibre of outstanding importance. It comes from the fibrous covering of the sheep, goat, camel etc. For thousands of year, wool has been used for clothing and other textiles by different tribes and nations around the world. Till today wool fibre has great importance because of its unique natural properties that are absent in other natural and synthetic fibres.
| Manufacturing Process of Wool |
The manufacturing process of wool
Shearing:
Shearing is the way toward gathering sheep wools. Predominant fleece choice originates from the edges and shoulders any place it develops we gather longer, better and milder and great quality wool. Chest, midsection and shanks fleece are as a subsequent downy.
Preparation:
Eight pounds of fleece from one sheep are stuffed into baggage or bunches. The other name of fleece or new sheared fleece is Grease fleece because it contains the regular oil of the sheep. It loses from twenty to eightieth of its unique load in the wake of washing.
Grading and sorting:
Grading is set by sort, length, fineness, snap and strength. Separating of fibre by bit and sight, sorting is done.
Scouring:
Raw wool is dirty and contaminated with natural substances that must be removed before processing can be carried out. It is washed or scoured by being agitated gently in tanks filled with warm water containing detergent then propelled gently through the tank, squeezed between rollers and carried into another tank. It may pass through four or more tanks until eventually it is rinsed in clean water.
Drying:
Wool subsequent to scouring ought not to be permitted to turn out to be completely dry. Around, 12 to16 percent of the dampness is left in the fleece which would empower treatment of the filaments in further handling.
Oiling:
Wool is unmanageable after scouring and hence the fibre requires to be treated with various oils to keep it from becoming brittle. Oiling of the fibres also helps to lubricate it for the spinning operation.
Garneting:
The picking and destroying procedure of reused and unused wool fibre is called garneting.
Carding:
The carding method introduces the classification of woollen yarns and worsted yarns. It makes the fibre parallel and removes a few quantities of dirt owing to straightening of fibres. Fibres for the worsted yarn are a lot of straighter than the woollen yarns.
Gilling and combing:
The checked fleece that will make into worsted yarn, place through gilling and combing tasks. The geilling technique evacuates the shorter staple and fixes the fibre. This technique expels short strands from one to four.
Roving:
The brushed wool in this type of an untwisted stand called the top is then drawn out into a roving.
Spinning:
The long strands, lying corresponding to each other in the brushed roving, are ready to stick firmly together on contorting to shape a fine solid worsted yarn.
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: