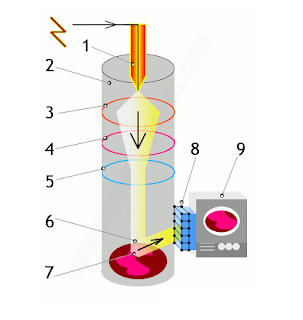
Working Principles:
X-rays are collimated and directed onto the sample. As the sample and detector are rotated, the intensity of the reflected X-rays is recorded. When the geometry of the incident X-rays impinging the sample satisfies the Bragg Equation, constructive interference and a peak in intensity occur. A detector records and processes this X-ray signal and converts the signal to a count rate which is then output to a device such as a printer or a computer monitor. Every crystalline substance gives a pattern; the same substance always gives the same pattern, and in a mixture of substances each produces its pattern independently of the others. The X-ray diffraction pattern of a pure substance is, therefore, like the fingerprint of the substance.
Applications:
- Crystal’s forms and unit cell parameters.
- The orientation of a single crystal.
- Different phases of samples.
- Element or compounds of a material.
Texpedi.com