Fabric strength testing?
Tensile strength testing: This is referred to as a strength test where the load is applied along the direction of the test sample. Tensile strength test of fabric is divided into two groups-
1. Strip test and
2. Grab test.
👉Strip strength test:
i. Five fabric samples are extended in a direction parallel to the warp and five parallel to the weft.
ii. The specimens are cut to a size of 2.5 inches in width and then removing threads from both edges until the width has been reduced to 2 inches.
iii. The test length should be 8 inches between the jaws and so enough extra length must be allowed for gripping in the jaws.
iv. Under optimum conditions, the specimen will be mounted centrally. Security gripped along the full width to prevent slipping.
v. The load is applied uniformly across the full specimen width till the specimen tear out.
vi. If a test specimen breaks within 0.25 inch of the line of contact of either of the pairs of jaws at a load less than the average of normal breaks, the result should not be used in the calculation.
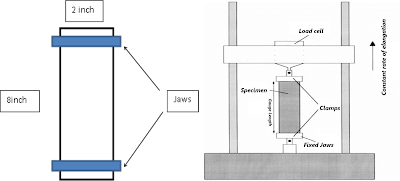 |
| Figure: An apparatus for fabric tensile strength test. |
👉Grab strength test:
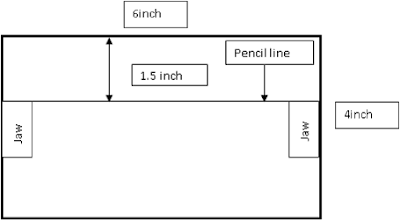
i. At first, we take specimen 4”x6”.
ii. Then the specimen is marked by a pencil at 1.5“from the edge of the specimen to assist in clamping it so that the same set of threads are clamped in both jaws.
iii. The two jaws are fixed on both sides of the specimen from 1” edge. This means that only the central 1 inch of the fabric is stressed.
iv. The gauge length used is 3 inch and the speed is adjusted so that the sample is broken in 20 ± 3s.
v. One jaw is fixed another jaw moveable.
vi. Then the moveable jaws start to move outwards till the specimen is tear-out.
 |
| Figure: Grab Test |
👉Tearing strength test:
Tear strength: Tear strength is the force required either to start or to continue the tear in a fabric under specific condition.
Tearing force: Tearing force is the average force required to continue a tear previously started in a fabric.
Tearing Resistance: Tearing resistance is one of the important properties of a textile fabric. The tear resistance of fabric indicates its resistance to tearing force.
Three types of tear test:
1. The tongue
2. Trapezoid
3. Elmendorf
👉Elmendorf:
Sample Preparation:
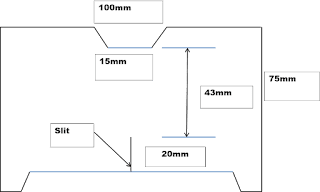
i. At first, we take specimen (100X 75) sq. mm.
ii. The template is placed on the specimen & cut according to the template as fig.
iii. A slit is created at the middle point at the specimen which range is 20 mm.
iv. In the test the Elmendorf continuous to tear the fabric from the end of the slit to the opposite edge a distance of 43 mm.
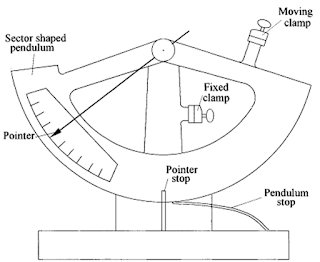
v. Pendulum lever principle is used here.
 |
| Figure: Elmendorf Tear Testing |
Working procedure:
• The apparatus consists of a sector-shaped pendulum carrying a moving sample clamp and the other clamp is fixed on the frame.
• When the pendulum is in the raised starting position, the specimen is fastened between the two clamps.
• The tear is started by a slit cut in the specimen between the clamps.
• The pendulum is then released and the specimen is torn as the moving clamp moves away from the fixed one.
• The pointer attached to the pendulum which is graduated to read the tearing force directly.
👉Bursting strength: This tear strength is basically used for knitted, lace, non-woven fabric, parachute fabrics, filters, sacks and nets etc. It is the uniformly distributed force over a given area applied to the fabric surface which is needed to break.
There are mainly two types of bursting strength test-
1. Hydraulic or Diaphragm burst
2. Ball burst
👉Hydraulic Bursting Tester:
 |
| Figure: Hydraulic bursting tester. |
Procedure:
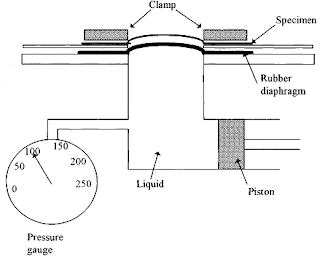
i. The pressure in a liquid is exerted in all directions and advantage is taken of this phenomenon in the hydraulic bursting tester.
ii. The specimen S is clamped by a ring over a thin flexible rubber diaphragm D, which is clamped over a circular hole in the upper face of a reservoir.
iii. The liquid used may be water or glycerin.
iv. The hydraulic pressure is increased, by valves or screw driven piston and the diaphragm distends taking with it the specimen.
v. At some point the fabric bursts, the pressure is indicated by the gauge G.
vi. Since the rubber diaphragm requires a certain pressure to stretch it, corrections may be made either by doing a blank test i.e. noting the pressure required to distend the diaphragm the same amount without the presence of fabric.
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles: