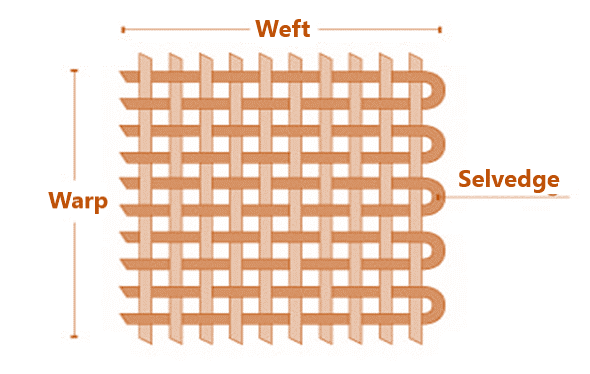
The technique, how the two series of threads (warp and weft) are interlaced at right angles to each other is called structure (/woven fabric structure). The structure is the interlacement of warp and weft yarn or interloping of loops. Woven cloth structure depends on the following factors:
- The nature /type of yarn used.
- The count or relative thickness of the yarns used as warp or weft.
- Thread density of the fabric.
- The order of interlacing the ends and picks.
- Modification produced by finishing treatment.
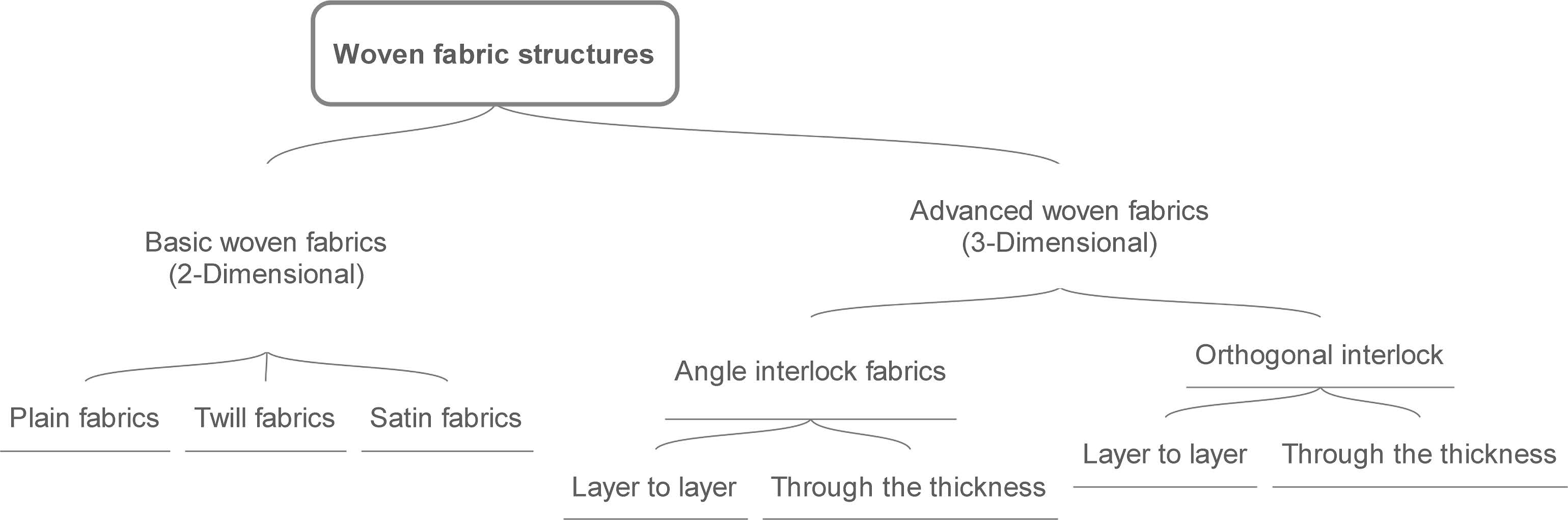
Classification of woven fabric structure?
Woven structures may be classified into 2 types as below-
- Simple Structure.
- Compound Structure.
Simple structure:
- Ends and picks intersect one another at right angles.
- There is only one series of warp and weft.
- All constituent threads are equally responsible for both the aspect of utility or performance in a fabric.
- Example: Plain, Twill fabric.
Compound structure:
- Maybe more than one series of ends or picks.
- Some of ends or picks may be responsible for the body of the fabric, such as ground yarns; some may be employed for ornamental purposes such as figuring or face yarns.
- Threads may project out at right angles to the general plane of the fabric.
- Example: Pile, Towel fabric.
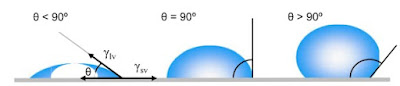
When a fabric is called on-grain?
A fabric that is on grain has warp yarns parallel to each other and perpendicular to the filling yarns that move straight across the fabric.
When a fabric is called off-grain?
When the angle of interlacement is less or more than 90 degrees then it is called off-grain. It is a fabric fault.
Texpedi.com
Check out these related articles:




2 thoughts on “Fabric Structure | Classification | On-grain | Off-grain”